Recovery Time Objective (RTO)


| ||||||||||||||||||||||
2. Period of time following an incident within which
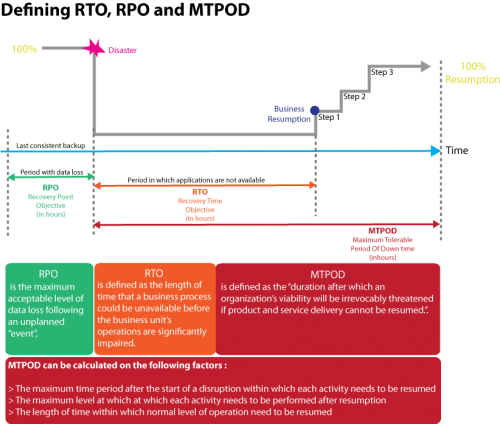
- Product or service must be resumed, or
- Activity must be resumed, or
- Resources must be recovered.
Note : For products, services, activities, the recovery time objective must be less than the time it would take for adverse impacts that would arise as a result of not providing a product/service or performing an activity to become unacceptable.
(Source: ISO 22301:2012 – Societal Security – Business Continuity Management Systems - Requirements) - clause 3.45
3. Target time set for resumption of product, service or activity delivery after an incident.
(Source: AE/HSC/NCEMA 7000:2021)

4. Target time set for resumption of product, service or activity delivery after an incident.
(Source: British Standard BS25999-1:2006 Code of Practice for Business Continuity Management)
5. The period of time within which systems, applications, or functions must be recovered after a disruption has occurred. For example, critical business functions must be restored within 4 hours upon occurrence of a disaster.
(Source: Singapore Standard 540 - SS 540:2008)
6. An essential output from the BIA that identifies the time by which Mission Critical Activities and/or their dependencies must be recovered.
(Source: Business Continuity Institute - BCI)
7. The period of time within which systems, applications, or functions must be recovered after an outage (e.g. one business day). RTOs are often used as the basis for the development of Business Continuity Strategy, and as a determinant as to whether or not to implement the Business Continuity Strategy during a disaster situation. SIMILAR TERMS: Maximum Allowable Downtime.
(Source: Disaster Recovery Institute International / Disaster Recovery Journal - DRII/DRJ)
(Source: Malaysia BCM Standard MS1970:2007)
8. The period of time required to fully re-establish adequate resource requirements.
(Source: HB 221:2004 Business Continuity Management)
(Source: Australia. A Practitioner's Guide to Business Continuity Management HB292 - 2006 )
9. The period of time required to fully re-establish adequate resource requirements to recover a critical activity, process, function, or other capability, to a required minimum operational level.
NOTE: The time required to recover capability to achieve the RPO may be additional to the RTO.
(Source: AS/NZS 5050.2 Australian and New Zealand Standards for business continuity management.
Part 2: Business continuity management practice standard)
10. The period of time within which systems, applications, or functions must be recovered after an outage (e.g. one business day).
(Source: Business Continuity Institute - BCI)
(Source: ENISA - the European Network and Information Security Agency. BCM & Resilience Glossary)