Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 14:01, 24 July 2024
1. Recovery Point Objective or RPO is the point in time to which systems and data must be recovered after a disaster has occurred.
 For example, data should be restored up till the start of the day. It includes the amount of data needed to be re-constructed after the systems or functions have been recovered. Simply explained, RPO:
{{#ev:youtube|43E6-2NUHiQ|400}} 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
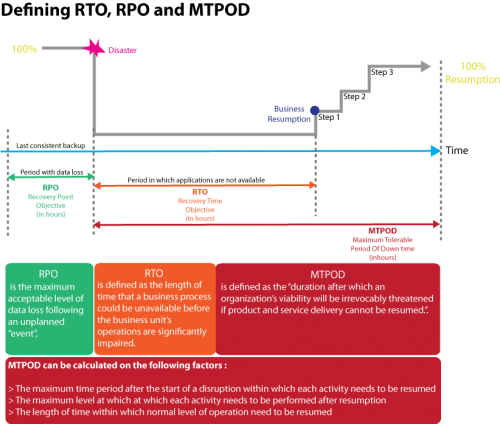
2. Point in which information used by an activity must be restored to enable activity to operate on resumption.

Note : Can also be referred to as "maximum data loss".
(Source: ISO 22301:2012 – Societal Security – Business Continuity Management Systems - Requirements) - clause 3.44
3. The point in time to which systems and data must be recovered after a disruption has occurred. For example, data should be restored up till start of the day.
(Source: Singapore Standard 540 - SS 540:2008)
4. The point in time to which work should be restored following a Business Continuity E / I / C that interrupts/disrupts the business e.g. ‘start of day’.
(Source: Business Continuity Institute - BCI)
5. The point in time to which systems and data must be recovered after an outage. (e.g. end of previous day's processing). RPOs are often used as the basis for the development of backup strategies, and as a determinant of the amount of data that may need to be recreated after the systems or functions have been recovered.
(Source: Disaster Recovery Institute International / Disaster Recovery Journal - DRII/DRJ)
(Source: Australia. A Practitioner's Guide to Business Continuity Management HB292 - 2006 )
6. The point in time to which systems and data must be recovered after an outage (e.g. end of previous day's processing). RPOs are often used as the basis for the development of backup strategies and as a determinant of the amount of data that may need to be recreated after the systems or functions have been recovered.
(Source: Malaysia BCM Standard MS1970:2007)
7. The capability at a pre-disruption point in time to which systems and data must be recovered after an outage (e.g. to end of previous day’s processing).
(Source: AS/NZS 5050.2 Australian and New Zealand Standards for business continuity management.
Part 2: Business continuity management practice standard)